Common Threats and Vulnerabilities That Lead to Data Breaches
Data breaches expose sensitive information and cause major damage. Learn about the key threats and vulnerabilities that lead to data breaches and how to protect your business.
Published July 28, 2025

Data breaches can cause serious damage to your business, often starting with overlooked threats and vulnerabilities that lead to data breaches. Understanding these risks is the first step to protecting your sensitive information and maintaining customer trust.
In this blog, we will explore the common vulnerabilities that attackers exploit, including technical flaws, insider risks, and human factors. We will also cover best practices to help you reduce exposure and strengthen your security posture.
» Strengthen your cybersecurity with KELA's expertise
What Is a Data Breach?
A data breach is an incident where unauthorized individuals access confidential data by taking advantage of a weakness in a system. This usually occurs when a threat actor uses an exploit to target a specific vulnerability.
To understand how a data breach unfolds, it's important to look at the three core components that often lead to one: threats, vulnerabilities, and exploits. These elements work together, and when they align, the risk of a breach significantly increases.
Element | Definition | Examples | Role in a data breach |
|---|---|---|---|
Threat | A threat is anything that could potentially cause harm to a system or its data. It often refers to people or events that try to access data unlawfully. | Hackers, insider threats, competitors, nation-state actors, malware, phishing attempts. | Identifies and targets a system with the intent to compromise it or access sensitive information. |
Vulnerability | A vulnerability is a flaw or weakness in a system’s hardware, software, processes, or human behavior that can be exploited. | Weak or reused passwords, missing software patches, open ports, and misconfigured cloud storage. | A vulnerability is what makes the system exposed or open to attack—it provides the entry point. |
Exploit | An exploit is the method or tool used by a threat actor to take advantage of a vulnerability in order to carry out an attack. | SQL injection, ransomware, phishing emails, brute-force password attacks, MitM attacks. | The exploit is the actual method used to break in. It turns the threat into a successful attack by using the system’s weakness. |
» Make sure you know the difference between a vulnerability, a threat, and a risk
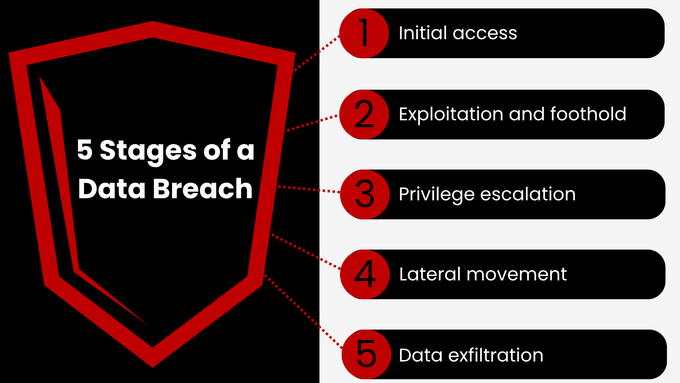
5 Stages of a Data Breach
Understanding how a data breach unfolds helps pinpoint where security efforts should be focused. Below is a breakdown of each stage—from the first point of entry to the final data theft.
1. Initial Access
The breach begins when attackers gain entry into a system or network. This is usually done by exploiting a known weakness, such as outdated software, misconfigured cloud infrastructure, or unpatched security flaws.
In many cases, phishing emails trick employees into handing over credentials, or attackers guess weak passwords through brute force. Sometimes, the breach is unintentional because it was triggered by insider mistakes or lost devices.
» Learn about five trends shaping Initial Access Broker activity
2. Exploitation and Foothold
After access is gained, the attacker strengthens their position within the environment. This stage involves deploying exploits to maintain access and prepare for further actions. Attackers may install remote access tools, bypass authentication layers, or abuse legitimate accounts.
If access was obtained from a third party (e.g., a vendor platform), they may quietly blend in using that partner’s permissions.
» Dive deeper with our guide to navigating third-party risks
3. Privilege Escalation
At this stage, the attacker attempts to gain higher levels of access within the environment. By exploiting poorly configured permissions, unused admin accounts, or gaps in access control logic, they move from a low-level user to someone with full administrative privileges.
The goal is to access sensitive systems, files, or backups that are otherwise restricted.
4. Lateral Movement
With elevated access, the attacker begins to move through the network. They scan for valuable assets—like file shares, internal databases, or user directories—and hop between systems using valid credentials or vulnerabilities.
Take Note: Lateral movement is often hard to detect because it mimics legitimate user activity. This is also where attackers identify where sensitive data is stored and plan exfiltration.
5. Data Exfiltration
This is the breach’s endgame—stealing the data. Attackers extract information in bulk or in stealthy increments to avoid triggering alerts.
They may use encrypted channels, disguise data transfers as normal activity, or send files to external cloud services. In some cases, exfiltration is paired with extortion threats (e.g., ransomware), even if no encryption is deployed.
» Here's everything you need to know about infostealers
Threats and Vulnerabilities That Lead to Data Breaches
Understanding the threats and vulnerabilities that lead to data breaches is essential for organizations looking to strengthen their security posture. Below, we explore the most frequent vulnerabilities and how they directly enable unauthorized access or data loss.
Technical Vulnerabilities
- Outdated software: Software that is not regularly updated leaves security holes open. Attackers exploit these flaws to bypass protections and install malware or gain control. Reports show a 180% rise in attacks targeting unpatched systems between 2023 and 2024.
- Weak passwords: Passwords that are easy to guess or reused across accounts give criminals a direct way to enter systems. Credential stuffing and brute force attacks take advantage of this vulnerability to compromise accounts and escalate access quickly.
- SQL injection attacks: This vulnerability targets website databases by inserting malicious SQL code into input fields. Attackers use SQL injection to bypass authentication, retrieve sensitive user data, or alter database contents without authorization.
- Cloud misconfigurations: Misconfigured cloud storage or services can unintentionally expose sensitive data publicly or to unauthorized users. Attackers often scan for these mistakes to get large amounts of information without needing advanced tools.
» Make sure you understand the difference between leaked credentials and compromised accounts
Identity and Access Management (IAM) Vulnerabilities
- Weak authentication practices: The absence of strong authentication—such as multi-factor authentication (MFA)—makes it easier for attackers to use stolen credentials. Weak or single-factor login systems remain a critical gap exploited in breaches.
- Excessive user permissions: Many users have more access rights than necessary, which increases risk if their accounts are compromised. Excessive permissions enable attackers or malicious insiders to access sensitive systems and data far beyond what’s required for their roles.
- Credential theft and compromise: Credential theft through phishing, malware, or insider threats remains a top cause of breaches. In 2022, the average cost per insider incident was $804,997, highlighting the financial risk posed by stolen or compromised login details.
- Failure to enforce least privilege: Not applying the principle of least privilege allows users and applications to hold more access than needed. This vulnerability facilitates privilege escalation attacks and widens the damage caused by breaches.
» Learn more: How to prevent phishing attacks
Human-Related Vulnerabilities and Exploits
- Phishing attacks: Phishing remains the most common attack vector, using deceptive emails, texts, or messages to trick users into revealing credentials or installing malware. These attacks frequently lead to credential theft and unauthorized access.
- Social engineering: Attackers manipulate people psychologically to disclose sensitive information or perform actions that compromise security. Social engineering exploits trust and can bypass technical defenses by targeting human weaknesses.
- Lack of security awareness: When employees lack training or understanding of security best practices, they become more susceptible to attacks. Negligence, such as clicking suspicious links or sharing passwords, increases breach risk.
Best Practices to Prevent Threats and Vulnerabilities That Lead to Data Breaches
- Comprehensive vulnerability management: Implement a continuous program that scans for weaknesses across all systems using dark web monitoring, automated malware detection, intrusion detection systems, and regular penetration testing.
- Automated patch management and configuration control: Maintain up-to-date software and hardware by automating patch deployment and regularly reviewing system configurations. This reduces the window of opportunity for attackers to exploit known vulnerabilities.
- Strong identity and access management: Enforce MFA, strong password policies, and strict access reviews. Apply the principle of least privilege and automate user provisioning and de-provisioning to reduce risks from excessive permissions and insider threats.
- Advanced data loss prevention and encryption: Use AI-powered Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tools integrated with security operations to detect unauthorized data movements and block potential exfiltration in real time.
- Employee training and security awareness: Conduct regular training focused on phishing prevention, social engineering, and secure handling of credentials. Empower employees to recognize and report suspicious activity.
- Network segmentation and zero trust architecture: Segment networks into smaller zones with strict access controls and continuously verify the identity of users and devices. This containment approach limits attacker movement and reduces the impact of any potential breach.
- Vendor and third-party risk assessments: Perform thorough security assessments of third-party vendors before onboarding and maintain ongoing monitoring. Limit third-party access strictly to what is necessary to reduce external risk exposure.
- Continuous monitoring: Deploy AI and machine learning-driven threat detection systems that monitor access logs, network traffic, and system behavior continuously. With KELA's platform recording a 200% increase in mentions of malicious AI tools in 2024, it's crucial to integrate these detection systems.
Take Note: The damage caused by a data breach often extends well beyond the initial incident. Reputational harm, legal penalties, business disruption, and ongoing attacker presence can all deepen the impact over time.
» Understand why you need cyber threat intelligence for your organization
How KELA Supports Your Business Against Data Breach Risks
We at KELA Cyber help your business identify and prioritize vulnerabilities based on real cybercriminal activity. Our AI-driven analysis of attack patterns and underground forums gives you early warnings and detailed insights into potential threats.
With tools like AiFort and proactive threat exposure reduction, we support your security strategy with actionable threat intelligence. Partnering with KELA Cyber means you get clear, practical information to protect your business from threats and vulnerabilities that lead to data breaches.
» Get started for free with KELA and strengthen your cybersecurity
Data Breach FAQs for Your Business
What causes a data breach?
A data breach happens when attackers exploit vulnerabilities in your systems, such as weak passwords, unpatched software, or cloud misconfigurations. It often requires a combination of a threat, a vulnerability, and an exploit coming together.
How do I prevent a data breach?
To prevent a data breach, keep your systems updated, enforce strong passwords and multi-factor authentication, and train employees on security best practices.
How does KELA help protect against data breaches?
KELA Cyber provides AI-driven threat intelligence by analyzing real cybercriminal activity in underground forums. This gives your business early warnings and detailed attack analysis.