Importance of Threat Intelligence in Consumer Fraud Detection
The digital age and rise of artificial intelligence has broadened the attack surface for consumer fraud, making everyone a potential target. Cyber threat intelligence might be the solution.
Published September 6, 2025

Consumer fraud is dominating the cybercrime sector recently, making up a significant portion of the 880,000+ complaints made by the American people in 2023. The sophistication of modern scams leveraging deepfakes and AI renders traditional authenticity checks obsolete, necessitating a paradigm shift towards continuous security vigilance. That's where threat intelligence platforms come into play.
» Skip to the solution: Try KELA Cyber for free
What Is Consumer Fraud?
Consumer fraud is a deceptive practice causing financial loss either to an individual or to an organization. Common types include:
- Phishing: Fraudulent attempts to obtain sensitive information (passwords, credit card details) by disguising as trustworthy entities in electronic communication (emails, messages)
- Identity theft: The illegal use of someone else's personal information (name, social security number, etc.) to gain financial advantage, open accounts, or commit crimes.
- Account takeovers: Unauthorized access and control of an individual's online account (bank, email, social media) by cybercriminals, often for malicious purposes.
- Online shopping scams: These scams involve fraudulent online retailers or sellers who may offer counterfeit goods, fail to deliver purchased items, or steal consumers' payment information through fake websites or deceptive practices.
- Imposter scams: These scams involve fraudsters impersonating trusted figures like government officials (IRS), credit bureaus, banking institutions, tech support representatives, or even family members to deceive victims into providing personal information or money.
» Here's how to prevent phishing attacks before they catch you
Real-World Cases of Consumer Fraud
Sony PlayStation Network Hack (2011)
A sophisticated attack compromised the personal data of 77 million PlayStation users. Attackers exploited network vulnerabilities, leading to significant financial losses and reputational damage for Sony.
The incident highlighted the need for robust security measures for online gaming platforms. Cyber threat analysts utilized social media to gather intel on events the attackers (Lizard Squad) announced on Twitter, helping them mitigate the DDoS traffic.
Target Data Breach (2013)
Hackers infiltrated Target's network through a third-party vendor, installing malware on point-of-sale systems. This resulted in the theft of credit card data and personal information of over 40 million customers, emphasizing the importance of third-party risk management and proactive security monitoring.
MGM Resorts Attack (2023)
A combined social engineering and ransomware attack crippled MGM Resorts' operations. Hackers gained access through a "vishing" scheme, deploying ransomware that disrupted critical systems and exposed customer data.
This incident underscored the need for employee cybersecurity awareness and robust incident response plans. MGM competitors received intelligence on the ransomware attack, helping them harden their defenses through the RH-ISAC intel sharing platform by importing indicators of compromise into their TIPs (threat intelligence platforms).
» Make sure you know about the key cyberthreats coming in 2025
Why Consumer Fraud Is So Difficult to Detect
The digital age has broadened the attack surface for consumer fraud, making everyone a potential target. Uncommon techniques have been amplified by AI, enabling mass-scale attacks through deepfakes, ransomware, and automated phishing campaigns that mimic legitimate interactions, deceiving even the most cautious of individuals.
The reliance on online transactions and digital identities creates a fertile ground for malicious actors. This constant connectivity mandates proactive security measures, including robust authentication, vigilant monitoring, and continuous consumer education.
» Confused about how hackers steal data? Here's all you need to know about infostealers
What Is Cyber Threat Intelligence?
Cyber threat intelligence (CTI) analysts gather and analyze information about how criminals target individuals, such as their methods for phishing, creating fake websites, or stealing personal data.
This intelligence helps businesses and security professionals understand the evolving tactics of fraudsters, enabling them to proactively protect consumers by identifying and mitigating potential threats before they result in financial loss or identity theft. Essentially, it's about staying one step ahead of the scammers with some key techniques:
- Data collection and analysis adds context to any received intel so that it is actionable and relevant to an organization’s business vertical.
- Effective dissemination to pertinent teams can help add to the existing security posture by integrating analyzed data into existing SIEMs and network security devices.
» Enhance your understanding of cybercrime with these most-targeted entry points by hackers
Benefits of Cyber Threat Intelligence for Battling Consumer Fraud
The primary measurable benefits of implementing CTI against consumer fraud include:
- Reduced chargeback rates: By identifying fraudulent activity before transactions are finalized, CTI helps stop unauthorized purchases from going through. This directly lowers the number of chargebacks your business has to process.
- Enhanced consumer trust: Proactive protection in against consumer fraud threats builds consumer faith in your business, leading to increased customer retention.
- Improved operational efficiency: Streamlined fraud prevention and effective threat intelligence automation allows you to optimize resource allocation and boost your company's efficiency.
Fine-Tuning IOC Collection Strategies
By meticulously tracking false positives (benign signals flagged as threats) and false negatives (missed threats), organizations gain critical data insights that allow for precise adjustments to IOC (indicators of compromise) collection strategies.
This helps ensure that threat intelligence focuses on the most relevant and accurate data, leading to a more efficient and effective fraud detection system.
Company-Wide Cost Savings
Effective threat intelligence can cut costs in several ways:
- Improved resource allocation: Evaluating the accuracy and reliability of both paid and open-source threat intelligence allows for informed decisions on resource allocation. By comparing the effectiveness of these sources, organizations can optimize their threat intelligence budget, potentially reducing costs while maintaining or improving the quality of their fraud detection capabilities.
- Fraud prevention: Effective threat intelligence proactively prevents fraud, thus minimizing financial losses.
- Reduced investigation durations: Faster detection and response times, enabled by accurate intelligence, reduce investigation durations and associated resource costs.
» Not convinced? Here are some more reasons your organization needs cyber threat intelligence
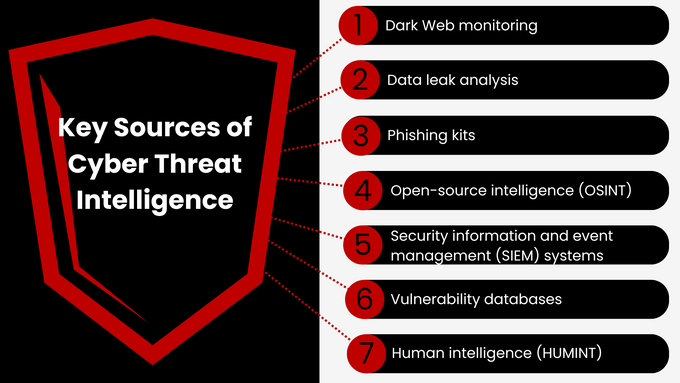
Key Sources of Cyber Threat Intelligence
By combining the following diverse sources, organizations can create a comprehensive threat intelligence program that enables them to proactively defend against cyber fraud and protect their consumers.
- Dark Web monitoring: Specialized tools and techniques are used to monitor underground forums, marketplaces like BreachForums, and hidden websites where threat actors often communicate, share exploits, and sell stolen data. Monitoring dark web forums for discussions about new malware strains, zero-day exploits, or compromised credentials can provide early warnings of potential attacks.
- Data leak analysis: Analyzing leaked or compromised data from various sources (past breaches, public repositories, etc.) to identify sensitive information that could be exploited by attackers and reveal patterns in compromised credentials helps organizations strengthen authentication measures and protect user accounts.
- Phishing kits: Collecting and analyzing phishing kits (tools used to create phishing websites) helps you understand the latest website templates, email lures, or social engineering tactics used to deceive victims. This enables organizations to educate users and update security controls.
- Open-source intelligence (OSINT): Leveraging publicly available information (news articles, social media, security blogs, etc.) can gather insights into emerging threats, vulnerabilities, and attacker activity.
- Security information and event management (SIEM) systems: Analyzing log data from security devices (firewalls, intrusion detection systems, etc.) can help identify suspicious activity and potential indicators of compromise like unusual login attempts or network traffic patterns associated with malware.
- Vulnerability databases: Referencing publicly available databases like the National Vulnerability Database helps keep you informed about known vulnerabilities in software and hardware.
- Human intelligence (HUMINT): Human sources (security researchers, industry experts, law enforcement, etc.) can offer insights into attacker motivations, tactics, and targets. Engaging with security researchers and participating in industry events can provide valuable information about emerging threats and attacker trends.
» Discover the differences between leaked credentials and compromised accounts
Catch Consumer Fraud Before the Breach With KELA
In the fight against ever-evolving consumer fraud, reactive measures simply aren't enough. Businesses need to adopt a proactive, intelligence-driven approach to protect consumers. This is where the power of comprehensive cyber threat intelligence shines.
KELA Cyber's unique capabilities include:
- Deep & dark web coverage with access to underground forums, marketplaces, and closed communities where threat actors congregate.
- Automated collection & analysis to gather and analyze vast amounts of data and integrate it into our Threat Actors Hub, providing real-time insights into cybercriminal activity.
- Connecting seemingly disparate data points, providing context that transforms raw data into actionable intelligence and enabling proactive identification of fraudsters and their schemes.
- Prioritizes the understanding of attacker motivations and methodologies, enabling organizations to predict and preempt fraudulent activities before they impact consumers.
- Integration & automation with existing security infrastructures, automating threat detection and response processes for efficient fraud mitigation.
In essence, leveraging robust threat intelligence platforms like KELA Cyber is not just a best practice; it's a necessity for any organization committed to protecting its consumers from the persistent and evolving threat of fraud.
» Ready to begin? Contact us to learn more or try KELA for free