How to Detect Password Leaks and Breached Credentials
Understand how KELA’s Identity Guard helps detect and prevent password and credential leaks with proactive monitoring and real-time alerts.
Published July 8, 2025

Breached credentials and password leaks aren’t the same—and it’s important to know the difference. Both can put sensitive data at risk, but credential breaches often involve a wider set of access details, making them more dangerous and harder to catch. In this blog, we’ll show you how to find leaked credentials early and share practical ways to detect issues before they escalate. By adopting proactive monitoring and detection strategies, you can stay ahead of security threats and better protect your organization’s data from breaches and unauthorized access.
» Get started for free with KELA and strengthen your cybersecurity
Understanding Password and Credential Leaks
Password leaks happen when just the passwords themselves are exposed to unauthorized parties. This could be due to weak security, data breaches, or accidental exposure.
Breached credentials are broader—they include not only passwords but also other authentication details like usernames, security tokens, or API keys. When these credentials leak, attackers can gain full access to accounts or systems.
While the two terms are often used interchangeably, it’s important to recognize that credential breaches pose a bigger risk because they provide more ways for cybercriminals to impersonate users and bypass security measures.
Password Leaks vs. Credential Breaches
| Aspect | Password leaks | Credential Breaches |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Only passwords are exposed, which limits what attackers can use. | Includes passwords plus usernames, tokens, and keys, giving broader access. |
| Risk | Attackers can access accounts if passwords are reused elsewhere. | Attackers may bypass additional security like two-factor authentication. |
| Example | A database breach revealing user passwords only. | Leaked session tokens, API keys, or full username-password pairs. |
| Impact | Can lead to unauthorized logins but may be blocked by extra security. | Can result in full account takeover and deeper system access. |
» Learn how to prevent phishing attacks before they catch you
4 Sectors Most Affected by Data Leaks and Credential Theft
- Financial companies, such as banks and insurance companies, are targeted due to potential financial gain through access to confidential accounts and information.
- Retail and wholesale companies are also targeted due to large volumes of customer data, making them lucrative targets for financial and identity theft.
- Healthcare is also a potential target due to confidential personal and medical information stored, which can lead to identity theft and financial gain.
- Governments are also targeted for information gathering, hacktivism, and potential financial gain.
» Make sure you understand the most targeted entry points by attackers
3 Methods to Detect Password Leaks or Breached Credentials
1. Credential Checking
Credential checking is a validated process used by cybersecurity providers to identify and confirm leaked or breached user credentials. It ensures that detection is accurate, secure, and compliant with privacy standards.
Key Features
- Database access: These services maintain databases of usernames and passwords from data leaks, typically from underground forums.
- Quick checks: Allows organizations and individuals to quickly check if their credentials are exposed to known breaches.
- Aggregated data: These services aggregate data from multiple sources, offering a simple and fast way to check for exposed credentials.
However, these services have limitations:
- Detection delays: These services generally offer a user-friendly platform, but they may not detect new breaches or identify new or targeted attacks quickly.
- Limited scope: They generally focus on publicly available data and may not detect internal system breaches or sophisticated attacks.
» Don’t overlook the real threat—learn how infostealers put your data at risk
2. Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) Gathering
OSINT is a method of collecting and analyzing publicly available information from various sources (surface web, social media, and deep web forums) to identify and analyze potential leaked credentials.
Key Features
- Breach insights: It helps identify leaks not widely reported, including breaches on niche forums or communities that may not be indexed by traditional sources.
- Data sharing and selling insights: Cybercriminals often share or sell compromised credentials on underground forums or dark web marketplaces, which OSINT can monitor for early detection.
3. Dark Web Monitoring
Dark web monitoring services track dark web markets and forums where compromised data, including credentials, is traded or discussed. This service provides access to information that cannot be easily discovered.
Key Features
- Specialized software and human analysis: These services use specialized software, and sometimes human analysts, to capture and analyze dark web content and correlate it with client assets.
- Understanding cyber threats: They inform us of the means cybercriminals use to acquire and monetize compromised accounts.
- Exclusive access to illicit markets: Dark web monitoring provides insights into compromised credentials that are traded or discussed in illicit dark web markets, which are not easily visible through traditional OSINT.
Take note: KELA's Identity Guard provides in-depth monitoring of the dark web and other illicit markets, offering insights into compromised credentials that are traded or discussed in these hidden spaces.
» Make sure you understand the difference between leaked credentials and compromised accounts
How KELA's Identity Guard Can Help You Find Password Leaks and Breached Credentials
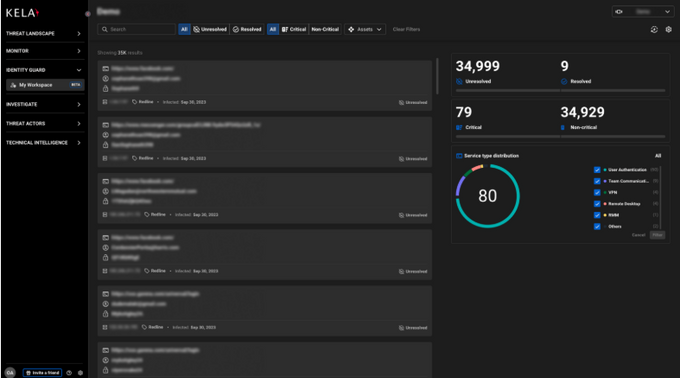
KELA's Identity Guard is a real-time identity protection platform that continuously monitors an extensive data lake containing hundreds of millions of compromised credentials.
Key Capabilities of the Platform
- Comprehensive source coverage: Monitors illicit dark web markets, cybercrime forums, instant messaging platforms, and bot markets.
- Digital asset discovery: Identifies compromised credentials associated with an organization’s assets.
- Real-time alerts: Notifications are generated when compromised credentials are discovered.
- Prioritization and classification: Automatically classifies the severity of alerts to prioritize remediation actions.
What to Do After a Password Leak: Short- and Long-Term Security Steps
When credential leaks or breaches are discovered, organizations must act swiftly to contain the damage and prevent further risks.
Short-Term Steps
- Reset affected passwords and ensure strong, unique passwords are set for compromised accounts.
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security for users with compromised credentials.
- Conduct a thorough investigation to understand the scope of the breach, including how credentials were exposed and what systems were impacted.
- Monitor systems for suspicious activity to detect any unusual access or data exfiltration related to the breach.
Long-Term Steps
- Review and strengthen security policies, including password management practices, and implement stronger measures if necessary.
- Conduct regular vulnerability scans to identify and address security weaknesses before they can be exploited.
- Provide ongoing employee training and awareness on cybersecurity best practices, including safe password management and phishing prevention.
- Set up continuous security monitoring to detect and address potential breaches in real-time.
Compliance Requirements Following a Password Breach
After a credential leak, organizations must consider regulatory obligations to avoid legal consequences.
Key regulations include:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) requires organizations to notify affected individuals and authorities within 72 hours of a breach.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) mandates healthcare entities to notify affected individuals if there’s unauthorized access to protected health information (PHI).
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) requires businesses handling credit card data to secure and protect customer information and notify affected parties in case of a breach.
» Learn more: How scary is that data leak, really?
Best Practices to Prevent Future Credential Breaches
- Implement continuous monitoring for compromised credentials to detect potential breaches early.
- Establish a robust security monitoring infrastructure to identify incidents quickly and pinpoint those responsible.
- Utilize real-time monitoring and alerting systems, potentially enhanced by AI, to detect suspicious behaviors and deviations from normal activity.
- Develop an effective incident response plan that includes a prepared team to handle security compromises efficiently.
- Prioritize proactive monitoring and strong security measures to reduce the risk of credential leaks and improve overall defense strategies.
Did you know? Using CanaryTokens can enhance your security strategy by providing early detection of breaches. These tokens act as proactive sentinels, detecting threats up to 10 times faster than traditional log-based methods. According to Cybenari, CanaryTokens offer a 92% faster breach detection rate than relying on logs alone, making them a valuable addition to layered, integrated security solutions.
Find Breached Credentials With KELA Cyber
Finding leaked credentials early is crucial in preventing data breaches and safeguarding sensitive information. With KELA’s Identity Guard, you gain access to real-time monitoring and detection of compromised credentials across multiple sources, including the dark web. Proactive alerts and continuous monitoring ensure that you stay ahead of threats, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access.
By using a comprehensive security approach, including dark web monitoring, OSINT, and compromised credential checking, KELA helps you find leaked credentials before they lead to significant harm.
» Ready to begin? Contact us to learn more or try KELA for free